
In the dynamic field of healthcare, nurses play a vital role in providing comprehensive and patient-centered care. One essential tool that aids nurses in delivering effective care is a Nursing Care Plan. A Nursing Care Plan serves as a roadmap, guiding nurses throughout their shifts and ensuring that they address the individual needs of each patient. This article delves deeper into the components, types, purpose, and process of developing a Nursing Care Plan, emphasizing the importance of this tool in promoting optimal patient outcomes.
Components of a Nursing Care Plan
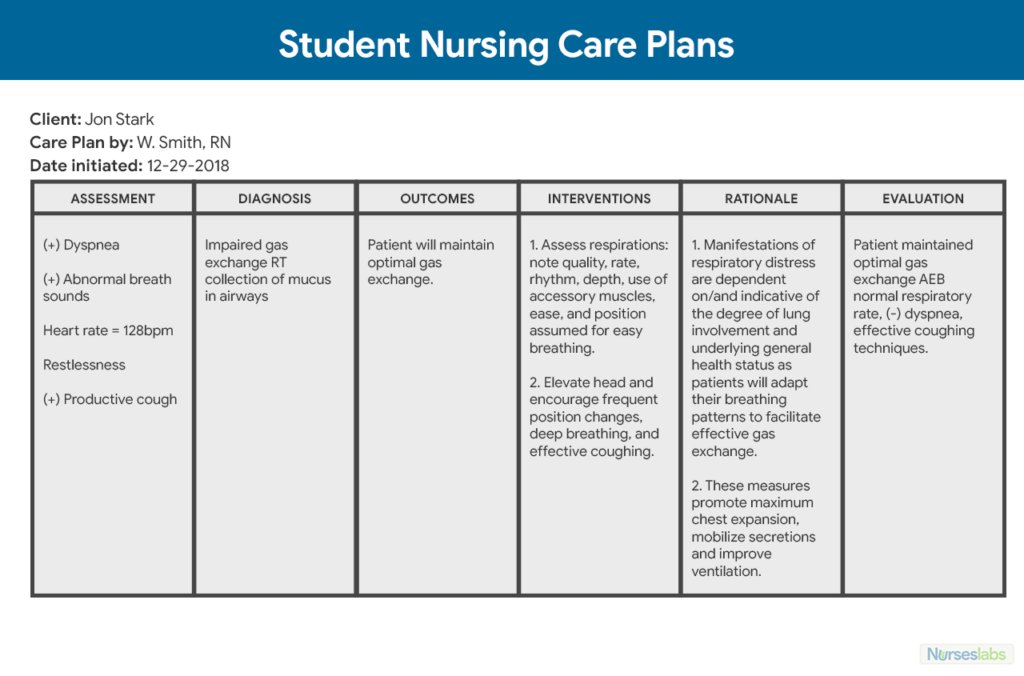
A Nursing Care Plan consists of several key components that provide a comprehensive view of the patient’s condition and the planned interventions. These components include assessment, diagnosis, expected outcomes, interventions, and rationale/evaluation.
- Assessment: The first step in developing a Nursing Care Plan is conducting a thorough assessment of the patient. This involves gathering subjective and objective data from various sources, such as the patient, family members, medical records, and physical examinations. Vital signs, medical history, current symptoms, and other relevant information are documented during this phase. The assessment phase forms the foundation for identifying the patient’s needs and developing appropriate interventions.
- Diagnosis: Using the data collected during the assessment phase, nurses formulate a nursing diagnosis. A nursing diagnosis is a clinical judgment that identifies potential or actual problems the patient is experiencing. These diagnoses are based on recognized taxonomies such as the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) and are aligned with Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Nursing diagnoses help prioritize treatments and interventions, ensuring that the most critical needs are addressed first.
- Expected Outcomes: After identifying the nursing diagnosis, nurses establish expected outcomes for the patient. Expected outcomes are specific, measurable goals that reflect the desired patient responses. These goals should be realistic, achievable, and patient-centered. They serve as benchmarks for evaluating the effectiveness of nursing interventions and the overall progress of the patient’s health.
- Interventions: Interventions are the specific actions and activities that nurses implement to address the identified nursing diagnosis and achieve the expected outcomes. These interventions are tailored to the individual patient’s needs and may involve a range of activities such as administering medications, providing patient education, assisting with activities of daily living, and monitoring vital signs. Nurses must ensure that interventions are evidence-based, safe, and aligned with best practices.
- Rationale and Evaluation: The rationale and evaluation component of a Nursing Care Plan focuses on the justification for selected interventions and the ongoing assessment of their effectiveness. Nurses document the rationale behind each intervention, explaining why it was chosen and how it relates to the patient’s specific needs. During the evaluation phase, nurses assess whether the desired outcomes have been met and make necessary adjustments to the plan as needed. Evaluation helps determine the effectiveness of the care provided and guides future interventions.
Types of Nursing Care Plans
Nursing Care Plans can be classified into four main types, each serving a specific purpose and addressing different patient scenarios.
- Informal Care Plans: Informal care plans exist in the nurse’s mind and are not formally documented. These plans are often used during the nurse’s shift and encompass the actions and interventions the nurse intends to accomplish. Informal care plans provide flexibility and adaptability in responding to the dynamic needs of patients.
- Formal Care Plans: Formal care plans are written or computerized documents that organize and coordinate the patient’s care information and plan. These plans provide a structured framework for documenting patient data, nursing diagnoses, expected outcomes, and interventions. Formal care plans facilitate communication among healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care across shifts and facilitating effective interdisciplinary collaboration.
- Standardized Care Plans: Standardized care plans are pre-established plans designed for groups of patients with similar healthcare needs. These plans are based on evidence-based practices and clinical guidelines and are frequently used for patients with common conditions or undergoing routine procedures. Standardized care plans streamline the documentation process, promote consistency in care, and enable nurses to provide efficient and effective interventions.
- Individualized Care Plans: Individualized care plans are tailored to the specific needs of an individual patient. These plans take into account the patient’s unique assessment data, medical history, preferences, and goals. Individualized care plans promote patient-centered care and ensure that interventions are customized to address the specific challenges and requirements of each patient.
Purpose of a Nursing Care Plan
Nursing care plans serve multiple purposes and have a significant impact on patient care and outcomes. The key purposes of a Nursing Care Plan include:
- Communication and Collaboration: Nursing care plans provide a means of communication and collaboration among nurses, patients, and other healthcare providers. By documenting the patient’s condition, nursing diagnoses, and planned interventions, care plans ensure that all team members are informed and working towards common goals. This promotes seamless care coordination and reduces the risk of errors or omissions in patient care.
- Holistic Care Approach: Nursing care plans enable nurses to adopt a holistic approach to patient care. By systematically assessing the patient’s physical, psychological, social, and emotional needs, nurses can develop comprehensive interventions that address the patient as a whole. This approach ensures that all aspects of the patient’s well-being are considered, enhancing the effectiveness of the care provided.
- Patient Advocacy: Nursing care plans promote patient advocacy by ensuring that the patient’s voice and preferences are heard and integrated into the care process. By involving patients in goal-setting and decision-making, nurses empower them to actively participate in their own care. Nursing care plans also provide a framework for documenting patient education and promoting health literacy, enabling patients to make informed choices about their healthcare.
- Quality and Safety: Nursing care plans contribute to the delivery of high-quality and safe care. By documenting evidence-based interventions, care plans promote standardized practices and adherence to best practices. They facilitate the identification of potential risks and guide nurses in implementing preventive measures and safety protocols. Nursing care plans also support the early recognition of changes in patient condition, allowing for timely interventions and reducing the risk of adverse events.
Process of Developing a Nursing Care Plan
Developing a nursing care plan requires a systematic and organized approach. While the process may vary slightly depending on the healthcare setting and individual patient needs, the general steps involve:
- Assessment: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the patient, collecting subjective and objective data from various sources, such as the patient, family, medical records, and diagnostic tests. This information forms the basis for identifying the patient’s needs and developing appropriate interventions.
- Diagnosis: Analyze the assessment data and identify the nursing diagnosis that best reflects the patient’s actual or potential problems. Nursing diagnoses should be specific, measurable, and aligned with evidence-based practices.
- Expected Outcomes: Establish clear and measurable expected outcomes that reflect the desired patient responses. These outcomes should be realistic, attainable, and patient-centered, promoting active patient involvement in goal-setting.
- Interventions: Based on the nursing diagnosis and expected outcomes, develop a plan of interventions that addresses the identified needs. Interventions should be evidence-based, safe, and tailored to the patient’s unique circumstances.
- Rationale and Evaluation: Provide a rationale for each chosen intervention, explaining why it is appropriate and how it relates to the patient’s specific needs. During the evaluation phase, assess the effectiveness of the interventions and document the outcomes achieved. Adjust the care plan as necessary based on the evaluation findings.
By following this systematic process, nurses can develop individualized and effective care plans that support optimal patient outcomes.
Sample Nursing Care Plan
To illustrate the practical application of a nursing care plan, let’s consider a sample case:
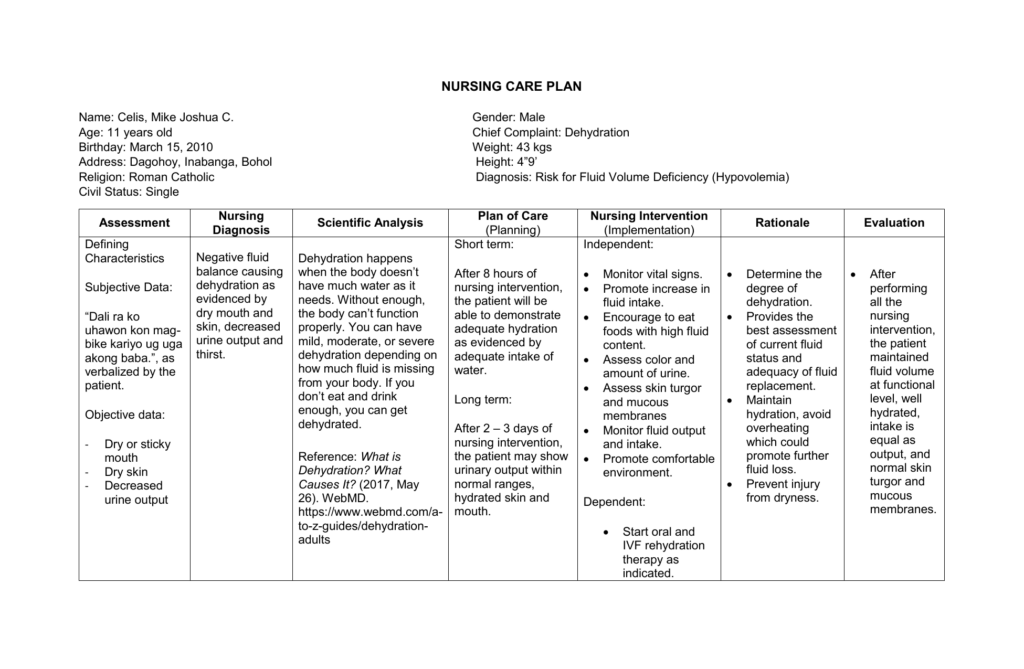
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Skin Integrity related to immobility and incontinence as evidenced by erythema, excoriation, and moisture on the sacral area.
Assessment:
- Perform a thorough skin assessment, noting the presence of redness, open areas, or signs of infection.
- Evaluate the patient’s mobility status, noting any limitations or restrictions.
- Assess the patient’s level of continence and the frequency of incontinence episodes.
- Consider the patient’s nutritional status and hydration levels, as these can impact skin integrity.
Expected Outcomes:
- The patient will maintain intact skin on the sacral area without signs of redness or excoriation.
- The patient will demonstrate an understanding of preventive measures for maintaining skin integrity.
- The patient will experience relief from the discomfort associated with impaired skin integrity.
Interventions:
- Reposition the patient every two hours to alleviate pressure on the sacral area.
- Implement a comprehensive skincare routine, including gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and application of protective barriers.
- Educate the patient and caregivers about the importance of maintaining skin hygiene and the use of appropriate products.
- Encourage the patient to increase fluid intake to promote hydration and skin health.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team to develop an appropriate nutritional plan to support optimal skin healing and maintenance.
Rationale and Evaluation:
- The repositioning interventions help alleviate pressure on the sacral area, reducing the risk of skin breakdown.
- The skincare routine and use of protective barriers create a barrier against moisture and irritants, promoting skin integrity.
- Patient education empowers the patient and caregivers to actively participate in maintaining skin health, reducing the risk of further damage.
- Monitoring the patient’s skin regularly and evaluating for changes or improvements helps assess the effectiveness of the interventions and guides any necessary adjustments to the care plan.
Frequently Asked Questions about Nursing Care Plans
- How can I effectively create a nursing care plan?
Developing a nursing care plan requires time and practice. You will learn this skill during nursing school and continue to utilize it throughout your nursing career. Here are the steps to follow: a. Perform a comprehensive patient assessment to identify the nursing diagnosis and gather pertinent patient data. b. Select a NANDA-approved diagnosis and establish both expected and projected outcomes for the patient. c. Implement the necessary interventions and assess if the desired outcome has been achieved. - What is the purpose of a nursing care plan?
Nursing care plans serve as a means of communication among nurses, patients, and other healthcare providers to collaboratively work towards achieving optimal healthcare outcomes. - What are the key components of a care plan?
The main components of a nursing care plan consist of the following: a. Assessment: Conducting a thorough evaluation of the patient’s condition and gathering relevant data. b. Diagnosis: Identifying the nursing diagnosis based on the assessment findings. c. Expected Outcomes: Setting measurable and realistic goals for the patient’s treatment. d. Interventions: Implementing appropriate nursing interventions to address the patient’s needs. e. Rationale/Evaluation: Providing the rationale behind the chosen interventions and evaluating the effectiveness of the care provided. - What information is included in a nursing care plan?
A nursing care plan includes essential details about the patient’s assessment, treatment goals, required interventions, and observations. These observations may encompass both subjective (patient-reported) and objective (observable) data.
Conclusion
Nursing care plans are essential tools that guide nurses in providing comprehensive, patient-centered care. By incorporating assessment data, nursing diagnoses, expected outcomes, interventions, and evaluation, these plans promote effective communication, holistic care, patient advocacy, and quality improvement. Nursing care plans play a crucial role in enhancing patient outcomes and ensuring the delivery of safe and evidence-based care. Through their diligent implementation and evaluation, nurses contribute significantly to the achievement of optimal health for their patients.
Credit source: https://nurse.org/